Description
As outlined in the video, native peptides naturally recognizing the target biomolecule (i.e. their cognate G-protein coupled receptor, GPCR) overexpressed on cancer cells serve as motifs for the design of peptide analogs. The latter may show improved characteristics, like higher stability or faster internalization in cancer cells. After elongation at the N-terminus by a spacer/linker, a suitable chelator is covalently attached for stable binding of a clinically relevant radiometal. Apt design of the above individual parts and their assembly in the final molecule is essential for the successful application of new radiopeptides in clinical oncology.
The labeling step actually allows for incorporation of a gamma emitting radiometal (e.g. Tc-99m, In-111) used in single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), or a positron emitter (e.g. Ga-68, Cu-64) for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging and a particle emitter (e.g. Lu-177) for radionuclide therapy.
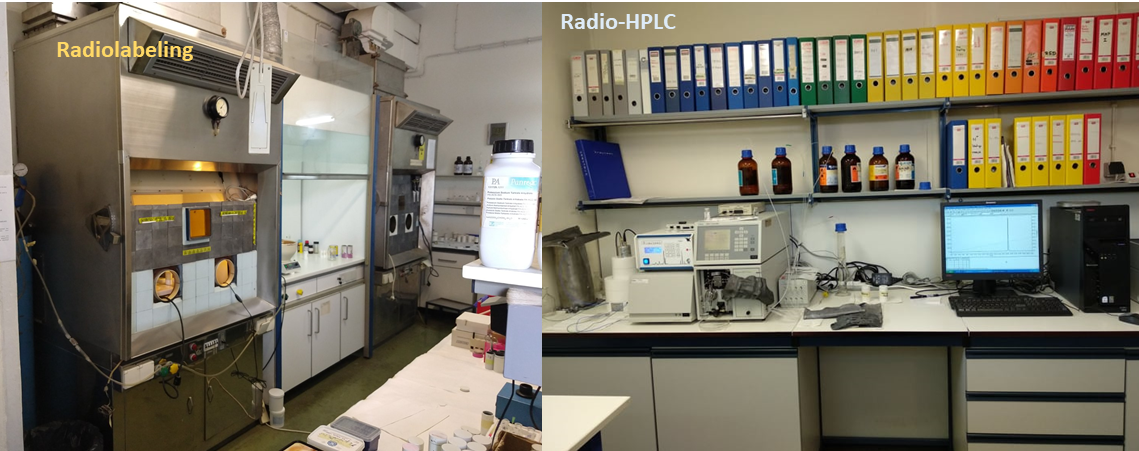
Radioanalytical methods applied next will provide information on the success of radiolabeling by determining radiolabeling yields and radiochemical purity. This step greatly relies on high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to UV and radio-detection modes. This step is essential for deciding whether or not the radioligand will be forwarded to the biological lab for further testing in cells or animals.
Furthermore, it is an essential part of the biological evaluation given that analysis of radiometabolites in biological fluids from animals (e.g. serum, urine, tissue homogenates) or cell preparations is actually conducted in the radioanalytical lab.
Since all manipulations with open radioactive sources and waste-management have to abide to international rules and guidelines, the radiolabeling-radioanalytical facility of Molecular Radiopharmacy is licensed and supervised by the Greek Atomic Energy Commission. Accordingly, for safe radiolabeling all manipulations are performed by trained and authorized personnel behind specially protected hoods; the radioanalytical lab is equipped with radio-HPLC units, radioactivity counters and all necessary and suitably protected devices.

Lead Scientist
Radiological Sciences & Radiopharmacy
See the list
Other Infrastructures
See all the Labs
See the list