INRASTES
Education Activities
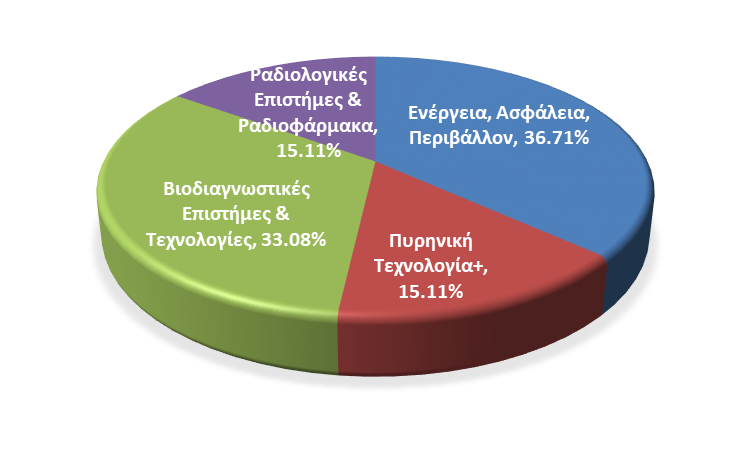
Education activities per Research Area
INRASTES has long reputation and strong commitment in postgraduate education and training, since the establishment of NCSR “Demokritos” in the 1960’s. Our research groups are involved in various education activities, including the supervision of graduate students, PhD candidates and junior postdocs, and running across the four different research pillars of the institute. In certain cases, postgraduate research projects can cover multiple pillars or be in collaboration with other institutes of “Demokritos”. A list of on-going and recently completed projects can be found below.
If you are interested in conducting your theses or training with us, please visit the corresponding sections:
Postgraduate and undergraduate teaching activities
Many of our researchers are invited lecturers in accredited postgraduate programmes organized by Universities in Greece and abroad, the Greek Atomic Energy Commission, and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Delivered courses range from Radiation Physics, Nuclear Reactor Safety, Nuclear Analytical Techniques, Industrial Safety, Environment and Solar Energy, to Radiopharmaceuticals, Clinical Chemistry, Molecular Diagnostics and Protein Chemistry.
Dissemination actions
Our research and education activities are disseminated to final year Science and Engineering students and graduates during the annual Summer School of NCSR “Demokritos”, in the form of lectures, laboratory demonstrations and tours.
In addition, we participate in the regular visits organized by the Education office of NCSR “Demokritos”, where we welcome several hundred high-school students visiting our laboratories per year. We also deliver lectures and conduct demonstrations addressed to the general public, e.g. during the annual festivities organized under the European Researchers Nights.
Video presentation of INRASTES education activities (in Greek):
INRASTES Education Officers
Dr Panagiota Petrou
(Biodiagnostic Sciences and Technologies; Radiological Sciences and Radiopharmacy)